Morphomics Data Dictionary
Jump to section:
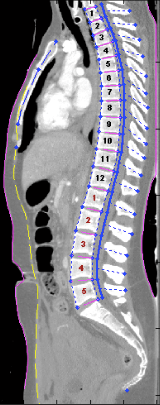
Overview
- This page describes morphomics measures available for every chest/abdomen/pelvis scan in our CT database.
- Most measures are taken "per vertebra" at each vertebral level visible in the CT scan, allowing morphomics to be reported as a function of body region.
- A number of measures of muscle density are reported in Hounsfield Units (HU), and often separated into Normal Density Muscle (NDM) and Low Density Muscle (LDM). The thresholds for these come from the paper: Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE, Wing RR, Meier A, Thaete FL. Effects of weight loss on regional fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in obesity. Diabetes. 1999;48(4):839-47.
- The "lean psoas" is a mathematical combination of measures of psoas cross sectional area (mm2) and psoas density (in HU) inside the muscle boundary. The formula for lean psoas is then:

This can be thought of as "normalizing a muscle's density between -85 HU (very fatty and low density) and +85 HU (very dense)". The values of ±85 were chosen by inspection of some of our sickest and healthiest individuals' data points.
Body Measures
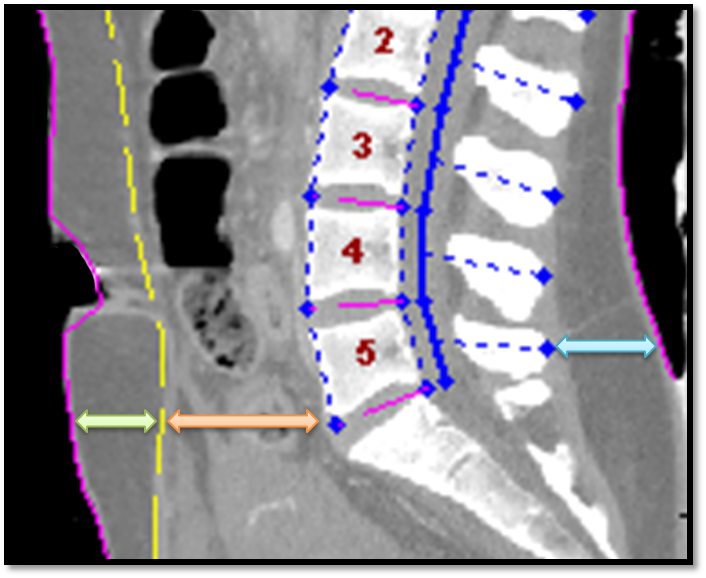
(central plane depths)
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| VB2FASCIA | mm | Distance - anterior of vertebral body to anterior fascia (central visceral depth) |
| FASCIA2SKIN | mm | Linear distance from anterior fascia to anterior skin (central sub-cutaneous depth) |
| SP2BACKSKIN | mm | Distance - posterior tip of spinous process to back skin (central back fat depth) |
Body Measures
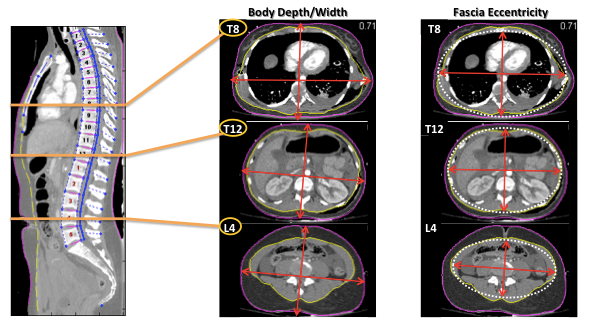
(shapes and sizes)
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| TOTALBODYAREA | mm² | Cross-sectional area of the body (area inside purple line) |
| FASCIAAREA | mm² | Cross-sectional area of the fascia region (area inside yellow line) |
| BODYDEPTH | mm | Front-to-back body distance (aligned to body habitus) |
| BODYWIDTH | mm | Left-to-right body distance (aligned to body habitus) |
| FASCIAECCENTRICITY | ratio | Eccentricity of an ellipse having the same second-moments of the fascia region. (Ratio of major-axis length to the distance between ellipse foci). A circle has eccentricity of 0, while a line has eccentricity of 1. |
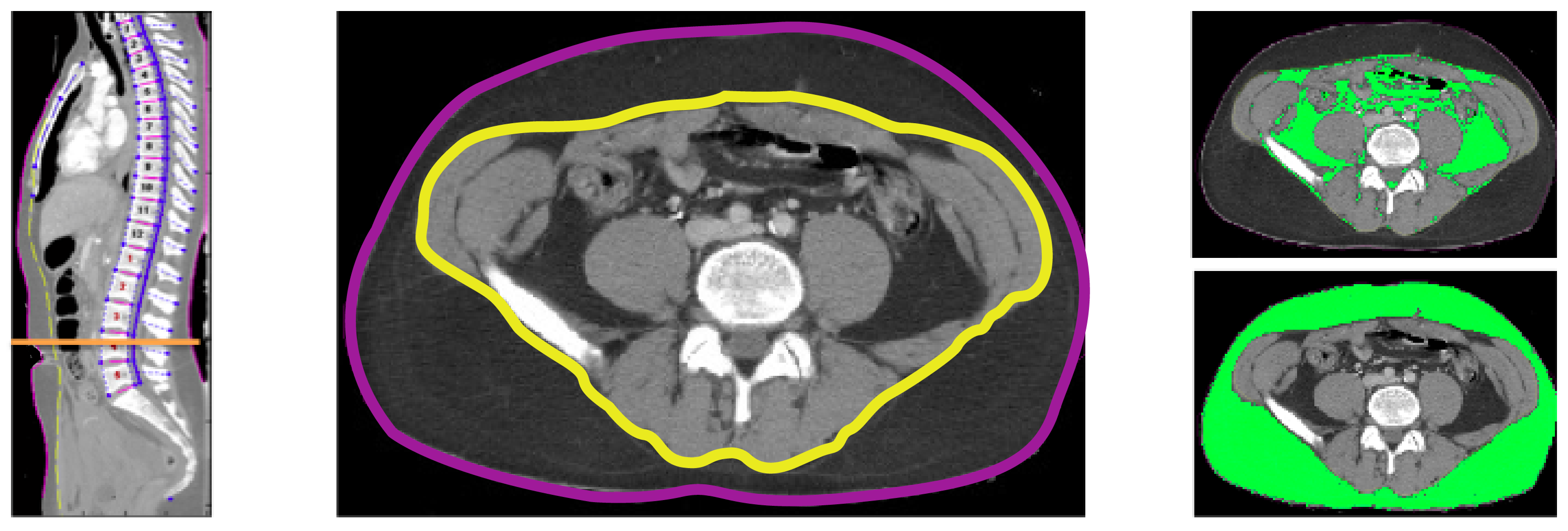
Fat Measures
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| VISCERALFATAREA | mm² | Area inside fascia (yellow line) meeting fat density thresholds (-205 to -51 HU) |
| SUBCUTFATAREA | mm² | Area between skin and fascia meeting fat density thresholds (-205 to -51 HU) |
| SUBCUTFATHU | HU | Median pixel intensity of fat-intensity pixels (-205 to -51 HU) in the subcutaneous region. Not computed when fewer than 200 pixels of fat exist. |
| VISCERALFATHU | HU | Median pixel intensity of fat-intensity pixels (-205 to -51HU) inside the visceral cavity. Not computed when fewer than 200 pixels of fat exist. |
Muscle
(skeletal)
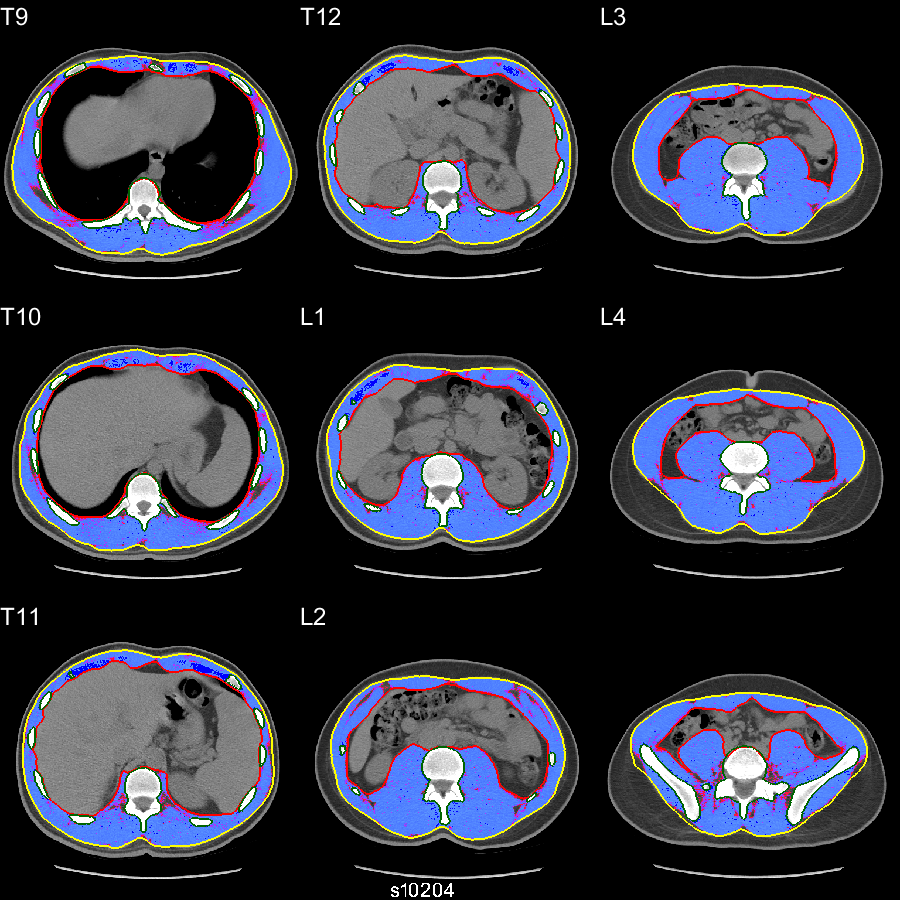
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| expmuscarea | mm² | Cross sectional area of the muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU, expanded range) between the muscle wall and fascia boundaries (excluding filled bone, spinal canal and disk). |
| vldmarea | mm² | Cross sectional area of the skeletal muscle falling in a very low density muscle HU range (-29 to -1). |
| ldmarea | mm² | Cross sectional area of the skeletal muscle falling in a low density muscle HU range (0 to 30). |
| ndmarea | mm² | Cross sectional area of the skeletal muscle falling in a normal density muscle HU range (30 to 100). |
| hdmarea | mm² | Cross sectional area of the skeletal muscle falling in a high density muscle HU range (100 to 150). |
| expmuscmeanhu | HU | Mean pixel intensity of the skeletal muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU) |
| expmuscmedhu | HU | Median pixel intensity of the skeletal muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU) |
| vldmmeanhu | HU | Mean pixel intensity of the very low density skeletal muscle pixels (-29 to -1 HU) |
| vldmmedhu | HU | Median pixel intensity of the very low density skeletal muscle pixels (-29 to -1 HU) |
| ldmmeanhu | HU | Mean pixel intensity of the low density skeletal muscle pixels (0 to 30 HU) |
| ldmmedhu | HU | Median pixel intensity of the low density skeletal muscle pixels (0 to 30 HU) |
| ndmmeanhu | HU | Mean pixel intensity of the normal density skeletal muscle pixels (30 to 100 HU) |
| ndmmedhu | HU | Median pixel intensity of the normal density skeletal muscle pixels (30 to 100 HU) |
| hdmmeanhu | HU | Mean pixel intensity of the high density skeletal muscle pixels (100 to 150 HU) |
| hdmmedhu | HU | Median pixel intensity of the high density skeletal muscle pixels (100 to 150 HU) |
Muscle
(psoas)
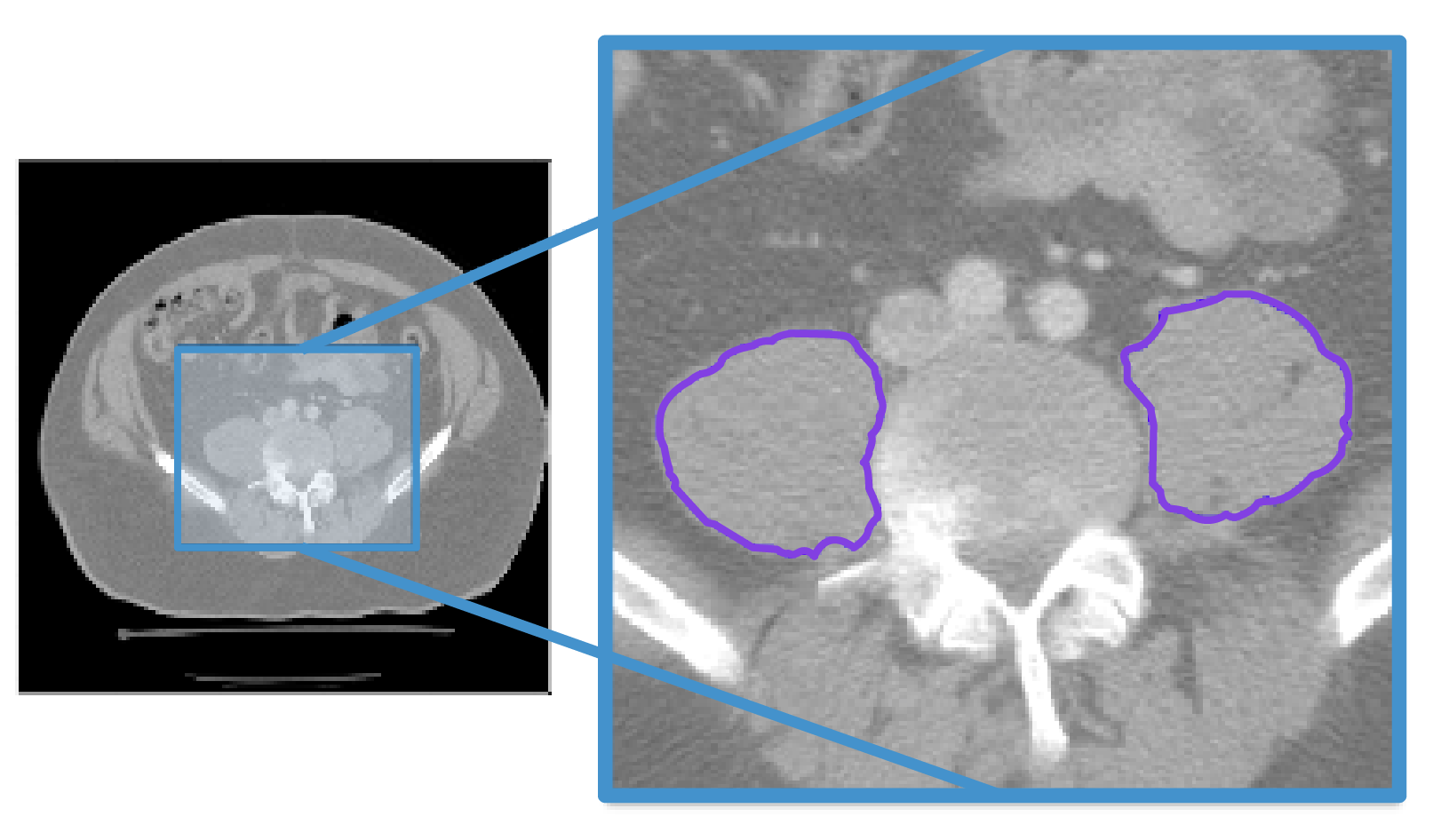
- The psoas muscles are core muscles running alongside the lumbar spine.
- Muscle size and density (indicative of fatty infiltration) have shown to be good indicators of subject frailty
- Psoas cross-section is sampled at the L4 vertebral level
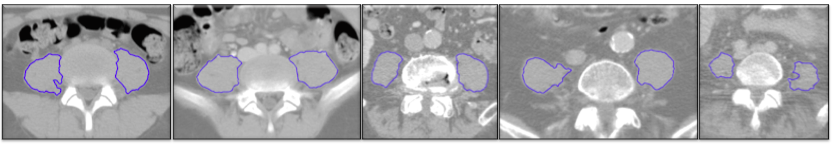
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| TOTAL_PSOAS_PERIMAREA | mm² | (TPA) Total area within the perimeter of the left and right psoas (region inside blue lines) |
| AVG_PSOAS_PERIMMEANHU | HU | Mean pixel intensity of all pixels inside blue lines |
| WEIGHTED_LEAN_PSOAS | HU*mm² | AVG_PSOAS_PERIMMEANHU normalized between -85 and +85, multiplied by TOTAL_PSOAS_PERIMAREA |
| TOTAL_PSOAS_EXPMAREA | mm² | (PMA) Cross sectional area of the muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU, expanded range) within the perimeter of the left and right psoas. |
Muscle
(dorsal muscle group)
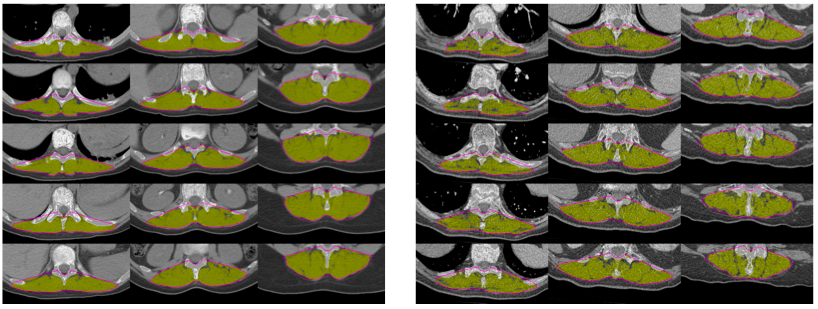
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| dmgvolofvb DMG Volume within VB |
mm³ | Volume of the dorsal muscle group between this vertebra and its superior neighbor |
| dmgperimarea DMG Boundary Area |
mm² | Cross sectional area of the DMG perimeter boundary IRRESPECTIVE OF bone/muscle/air contents. Boundary is built from triangle between spinal canal and left/right lateral seams, connected by nearest location to the posterior fascial envelope. |
| dmgexpmarea DMG Muscle Area |
mm² | Cross sectional area of the muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU, expanded range) within the DMG perimeter. |
| dmgldmarea DMG Low Dens. Area |
mm² | Cross sectional area of the DMG falling in a low density muscle HU range (0 to 30) |
| dmgndmarea DMG Normal Dens. Area |
mm² | Cross sectional area of the DMG falling in a normal density muscle HU range (31 to 100) |
| dmgexpmmeanhu DMG Mean HU |
HU | Mean pixel intensity of muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU) within the DMG boundary. |
| dmgexpmmedhu DMG Median HU |
HU | Median pixel intensity of muscle pixels (-29 to 150 HU) within the DMG boundary. |
| dmgldmmeanhu DMG Low Dens. Mean HU |
HU | Mean pixel intensity within Low Density Muscle (0 to 30) pixels inside the DMG boundary. |
| dmgldmmedhu DMG Low Dens. Median HU |
HU | Median pixel intensity within Low Density Muscle (0 to 30) pixels inside the DMG boundary. |
| dmgndmmeanhu DMG Normal Dens. Mean HU |
HU | Mean pixel intensity within Normal Density Muscle (31 to 100) pixels inside the DMG boundary. |
| dmgndmmedhu DMG Normal Dens. Med HU |
HU | Median pixel intensity within Normal Density Muscle (31 to 100) pixels inside the DMG boundary. |
Pelvis
(sizes)
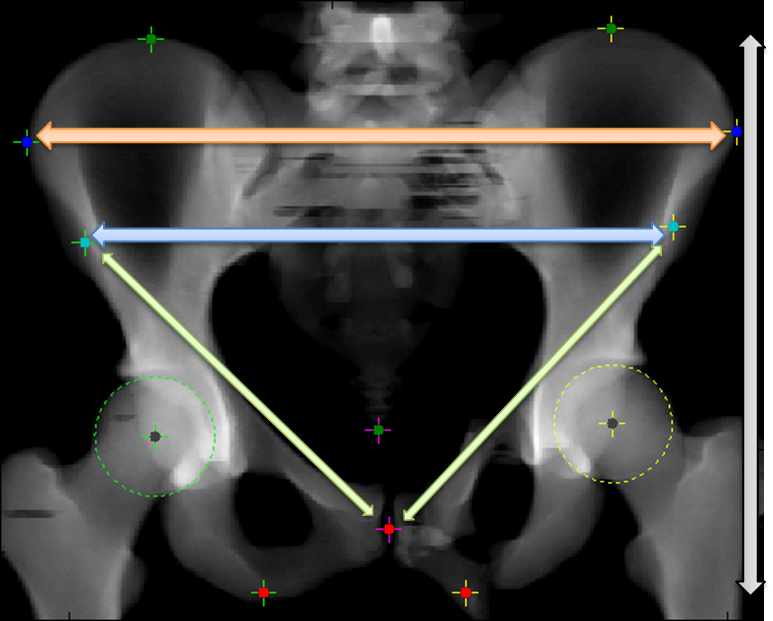
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| DIST_WINGLATPT2WINGLATPT | mm | Distance across full pelvis (shown in orange) |
| DIST_ASISPT2ASISPT | mm | Distance across ASIS (where the seatbelt goes, shown blue) |
| DIST_LASISPT2PUBISPT | mm | Distance from pubis to ASIS (shown green) |
| ANG_LASIS_PUBIS_RASIS | deg | Angle between two green arrows |
| PHEIGHT | mm | Height of pelvis (vertical arrow, shown grey) |
Spine Measures
(angles and sizes)
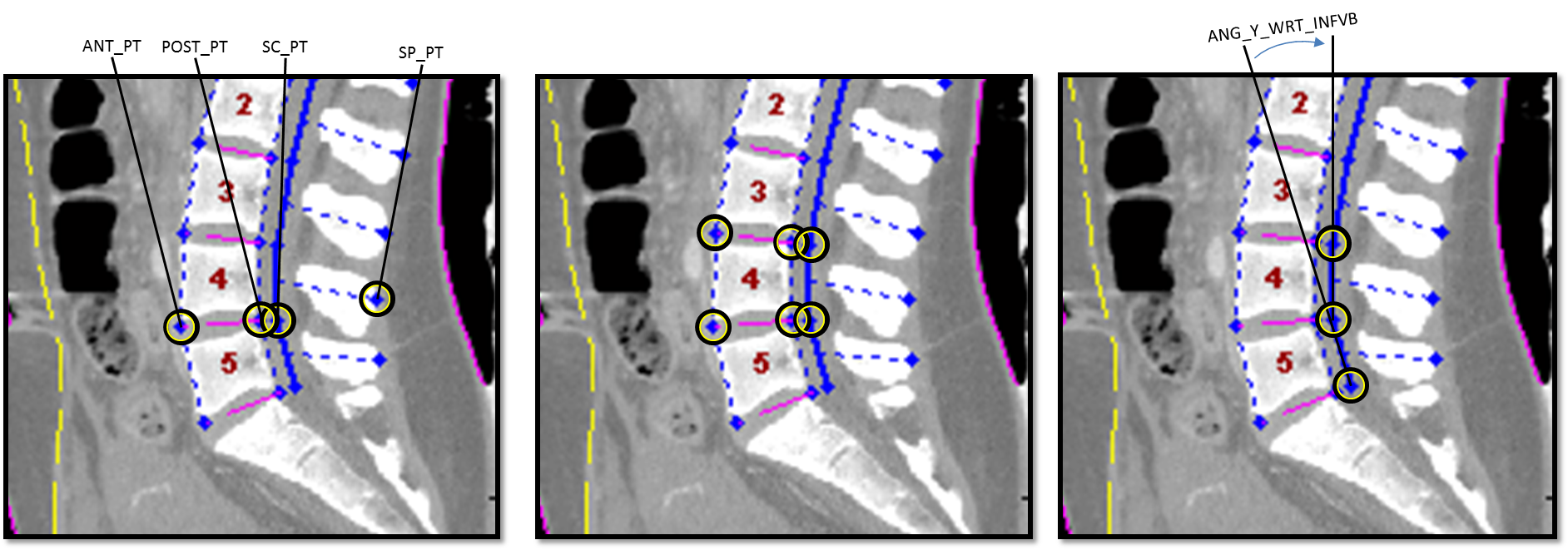
- For every vertebra (L4 shown in image) we record points on the inferior aspect:
- Spinal Canal Point (SC_PT)
- Anterior Vertebral Body Point (ANT_PT)
- Posterior Vertebral Body Point (POST_PT)
- On the posterior aspect:
- Spinous Process Point (SP_PT)
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| DIST_ANTPT2POSTPT | mm | Vertebral depth |
| DIST_INFSCPT2SUPSCPT | mm | Vertebral height at the spinal canal |
| DIST_INFANTPT2SUPANTPT | mm | Vertebral height at the anterior of the body (inclusive of disc) |
| ANG_Y_WRT_INFVB | deg | Vertebral angle (forward/backwards or flex./extension) with respect to the inferior vertebra (illustrated above) |
| ANG_X_WRT_INFVB | deg | Vertebral angle (side-to-side) with respect to the inferior vertebra (not shown above, will be zero for a laterally symmetric spine) |
| ANG_Y_WRT_YZ | deg | Vertebral "pose" (forward/backwards or flex./extension) with respect to the scanning table |
Spine Measures
(cortical bone)
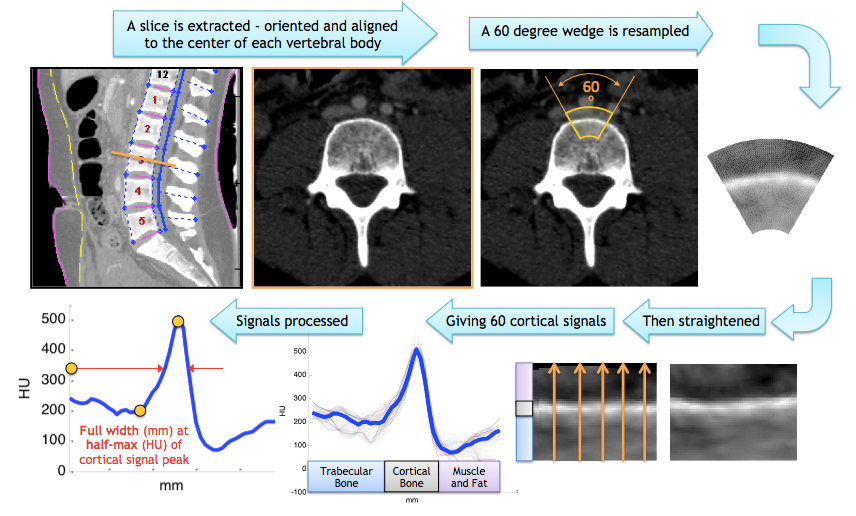
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| ANTCORTHMHU | HU | "Anterior Cortical Half-Maximum Hounsfield Unit" - HU level at half-max of the bone signal peak |
| ANTCORTFWBYHM | HU*mm | The "Full-width-multiplied-by-half-max" of the avg. cortical bone signal (Newman - 1998, Prevrhal - 1999) |
| ANTCORTFWBYHMSTD | HU*mm | Std. Dev. from all 60 "Full-width-by-half-max" measurements (at 1° increments in the 60° wedge) |
Spine Measures
(trabecular bone)
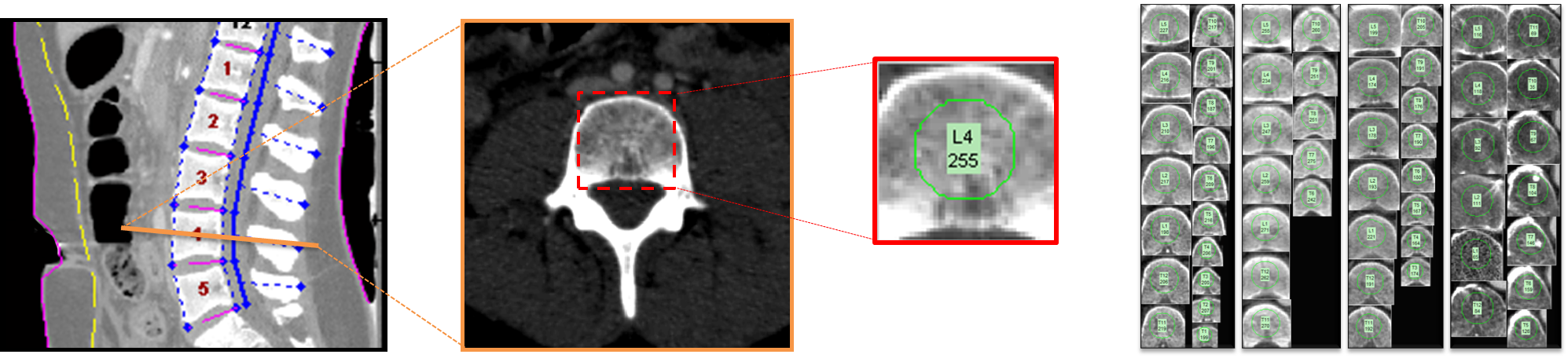
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| BMDHUVBALIGNED | HU | Average pixel intensity (in CT Hounsfield Units) inside central bone core sample |
Let's Collaborate
Morphomics is incredibly collaborative in nature, and its true power comes from bringing together experts and data from many fields to tackle important questions about human health and well-being.